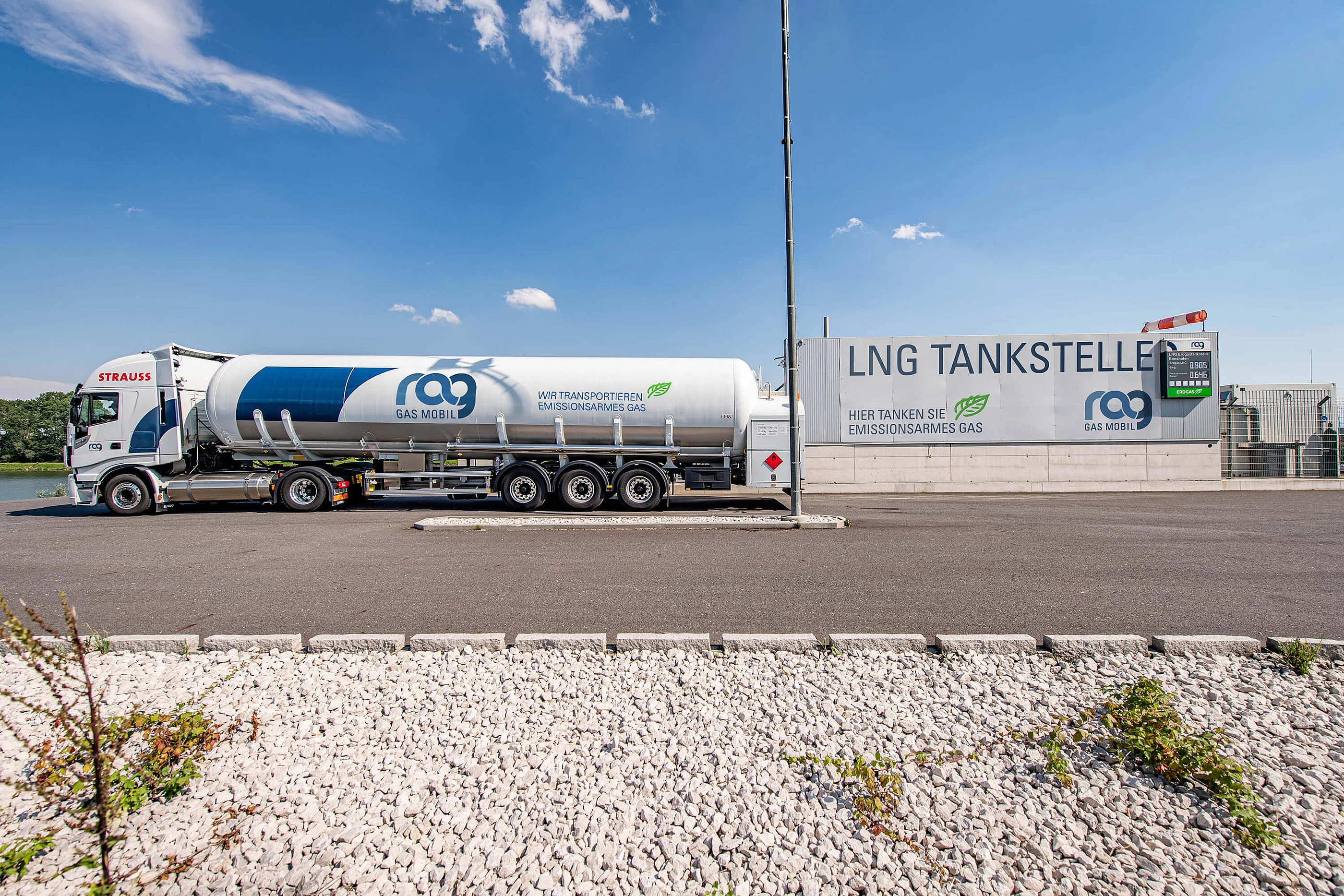
LNG - Liquefied Natural Gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been converted to a fluid aggregate state by cooling it to a temperature of around -163°C. Liquefaction makes it possible to transport and store 600 times as much energy in the same space. For this reason, LNG is primarily used for transportation of large volumes of energy over long distances, but also as a fuel for heavy goods vehicles and shipping. The gas can be produced in Austria or transported to customers here in specially designed road, barge and sea-going tankers. LNG has other big advantages: it is very economical and efficient.

 ©
©
Advantages of trucks that run on LNG
- Up to 20% less carbon dioxide emissions compared to diesel trucks
- 95% reduction in fine particulates
- Over 70% reduction in nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2)
- No AdBlue/catalytic convertor needed
- LNG technically mature for use in industry and heavy goods vehicles, and available for the long term
- Using LNG as a fuel reduces noise emissions by about 50%
- Infrastructure is under implementation along the LNG Blue Corridors – principle routes for LNG heavy goods vehicles in Europe
LNG – the fuel of the future
Transportation plays an essential role in a functioning economy. Medium- and long-term forecasts predict growth in the volume of road traffic, especially heavy goods traffic.
Global, European and national climate protection targets aim at a reduction in emissions produced by vehicles. The use of gas as a fuel can make a major contribution to achieving these targets, since vehicle traffic contributes about 45% of emissions. Numerous EU initiatives are promoting the import and use of LNG. This alternative fuel offers an immediately available technology with many environmental benefits for heavy-goods transport. In future, gas produced from renewable sources (LBG/bio-LNG) might also be used in addition to conventional natural gas.
LBG – Liquefied biogas
Chemically speaking, liquefied biogas (LBG) or bio-LNG is liquid methane, and thus identical to LNG and open to exactly the same uses; the difference is that it comes from renewable sources.
 ©
©
Energy supply for the future
For years, RAG has been working on innovative solutions that take account of changes in energy policies and the situation in the energy industry. And for a number of years now, RAG has been using its expertise to carry out research into power to gas technology. This will make it possible to convert excess renewable wind and solar energy into gas, which can be stored in natural underground gas reservoirs. We firmly believe that gas can make an important contribution to meeting climate protection targets, because of its flexibility and range of uses – for heating and transportation, and in industry.
As a result, RAG is committed through targeted investments, including in the development of infrastructure for the alternative fuel LNG.
Commissioning of our first LNG filling station, at Ennshafen port in September 2017, was the first milestone in this process, followed by the LNG filling stations in Graz and Ort im Innkreis which were implemented with local cooperation partners.
 ©
©
Safety
LNG is safe throughout the entire supply chain. Years of experience from industrial application shows that LNG does not present any greater risk than conventional fuels, which are transported every day – provided gas standards are complied with. LNG transportation fuel systems meet the same high safety standards as conventional systems. The design of LNG tanks differs fundamentally from that of tanks for conventional transportation fuel. LNG tanks are optimally protected against mechanical and thermal influences thanks to their compressive strength and tank-in-tank systems with integrated insulation.
